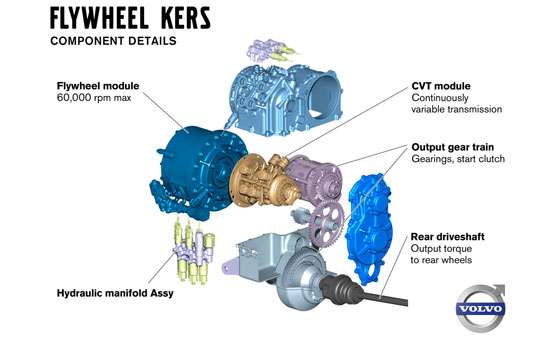
No KERS da Volvo, o volante de inércia, feito de fibra de carbono, com 19,91 cm de diâmetro, 5,9 Kg de peso, e capaz de girar a 60.000 RPM, é acoplado e desacoplado do eixo traseiro através de uma caixa de câmbio com relações continuamente variáveis (CVT). Quando o pedal do freio é acionado, o câmbio CVT aciona o volante, que ganha velocidade de rotação, enquanto o carro é frenado.
Enquanto os pedais do acelerador e do freio não são pressionados, o câmbio CVT desacopla o eixo traseiro do volante de inércia, que fica girando, sem, contudo, perder muitas rotações com o tempo, já que roda no vácuo, praticamente sem qualquer resistência.
A Volvo ressalta que o sistema criado pela marca sueca não só ajuda a economizar combustível como a potência resultante da junção "motor a combustão + KERS" é aumentada em 80 CV. A empresa acredita que o sistema é mais eficiente em arrancadas, mas que está fazendo o possível para tornar seu KERS mais eficiente.
O Volvo planeja começar a testar seu KERS em seus carros no segundo semestre de 2011, e está confiante de que pode reduzir o consumo de combustível em até 20%, usando um motor de quatro cilindros, em vez de um propulsor de seis cilindros.
A light, cheap and very eco-efficient solution that makes a four-cylinder engine feel like a six at the same time as fuel consumption drops with up to 20 percent. This autumn, Volvo Car Corporation will be one of the world's first car makers to test the potential of flywheel technology on public roads. The company has received a grant of 6.57 million Swedish kronor from the Swedish Energy Agency for developing next-generation technology for kinetic recovery of braking energy in a joint project together with Volvo Powertrain and SKF.
"Our aim is to develop a complete system for kinetic energy recovery. Tests in a Volvo car will get under way in the second half of 2011. This technology has the potential for reducing fuel consumption by up to 20 percent. What is more, it gives the driver an extra horsepower boost, giving a four-cylinder engine acceleration like a six-cylinder unit," relates Derek Crabb, Vice President VCC Powertrain Engineering.
60,000 revs per minute
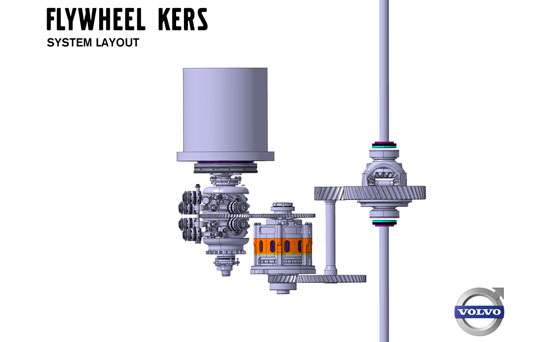
The new system, known as Flywheel KERS (Kinetic Energy Recovery System), is fitted to the rear axle. During retardation, the braking energy causes the flywheel to spin at up to 60,000 revs per minute. When the car starts moving off again, the flywheel's rotation is transferred to the rear wheels via a specially designed transmission.
The combustion engine that drives the front wheels is switched off as soon as the braking begins. The energy in the flywheel can be used to accelerate the vehicle when it is time to move off once again, or to power the vehicle once it reaches cruising speed.
"The flywheel's stored energy is sufficient to power the car for short periods. However, this has a major impact on fuel consumption. Our calculations indicate that the combustion engine will be able to be turned off about half the time when driving according to the official New European Driving Cycle," explains Derek Crabb.
Since the flywheel is activated by braking and the duration of the energy storage - that is to say the length of time the flywheel spins - is limited, the technology is at its most effective during driving featuring repeated stops and starts. In other words, the fuel savings will be greatest when driving in busy urban traffic as well as during active driving.
If the energy in the flywheel is combined with the combustion engine's full capacity, it will give the car an extra boost of 80 horsepower, and thanks to the swift torque build-up this translates into rapid acceleration, cutting 0 to 100 km/h figures significantly.
Carbon fibre for a lightweight and compact solution
Flywheel propulsion assistance was tested in a Volvo 240 already back in the 1980s, and flywheels made of steel have been evaluated by various manufacturers in recent times. However, since a unit made of steel is large and heavy and has rather limited rotational capacity, this is not a viable alternative.
The flywheel that Volvo Car Corporation will use in its test car is made of carbon fibre. It weighs about six kilograms and has a diameter of 20 centimetres. The carbon fibre wheel spins in a vacuum to minimise frictional losses.
"We are not the first manufacturer to test flywheel technology. But nobody else has applied it to the rear axle of a car fitted with a combustion engine driving the front wheels. If the tests and technical development go as planned, we expect cars with flywheel technology to reach the showrooms within a few years," says Derek Crabb. He concludes: "The flywheel technology is relatively cheap. It can be used in a much larger volume of our cars than top-of-the-line technology such as the plug-in hybrid. This means that it has potential to play a major role in our CO2-cutting DRIVe Towards Zero strategy."

Postar um comentário